qunit-helpful
QUnit plugin to automatically show helpful info for failed assertions
Test page, tests with variable injection
Example:
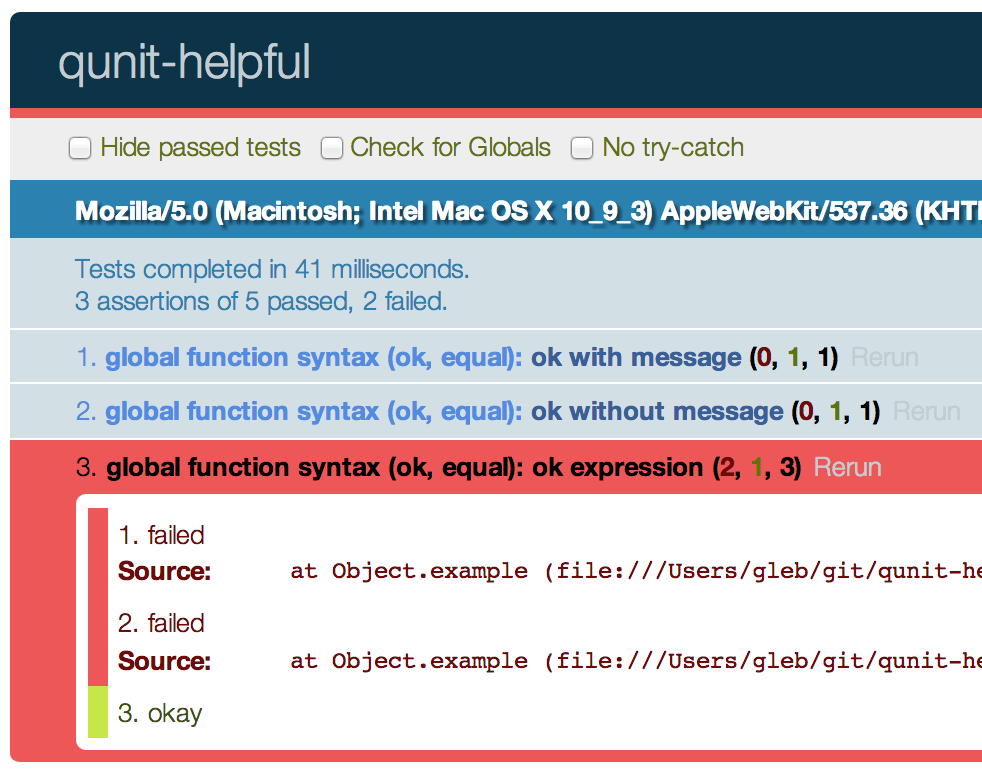
// QUnit test with failing assertionQUnit; // output Errors: Module: global Test: simple test // load qunit-helpful.js before tests, same test// output Errors: ok 2 + 2 === 5 Module: global Test: simple testComparison screenshots with the failed assertions for source
QUnit;QUnit with failed ok(expression)
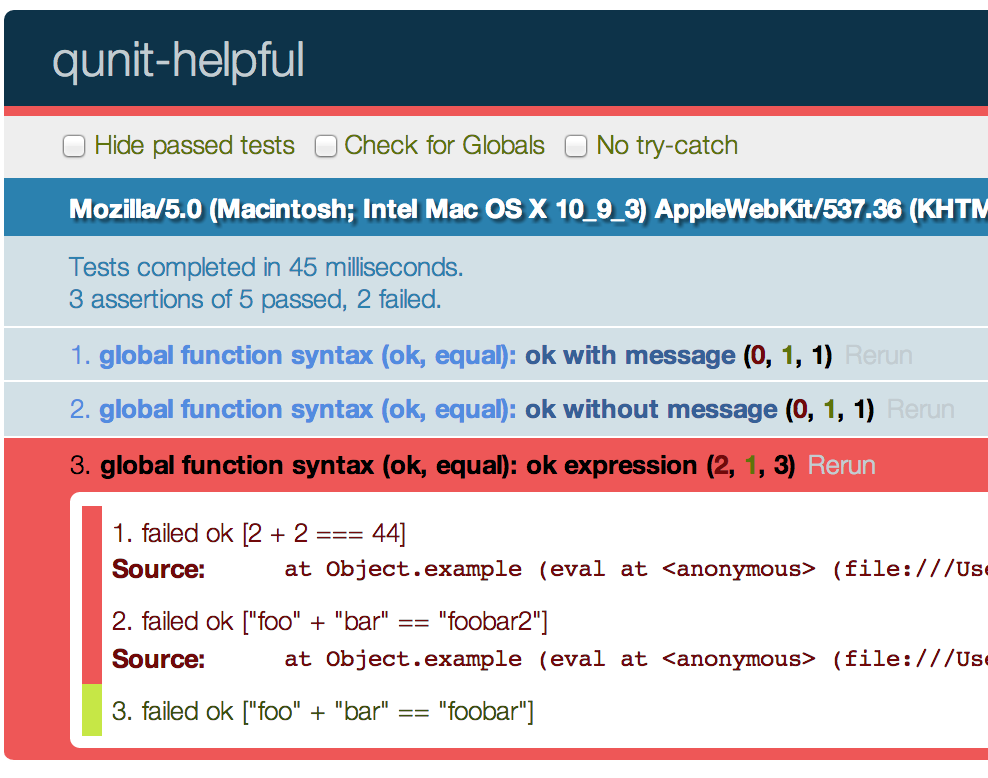
QUnit + qunit-helpful with failed ok(expression)
Supported assertions
This package rewrites ok, QUnit.ok, equal, QUnit.equal assertions, leaving the rest of the
code unchanged. I might add other QUnit assertions
if needed.
Explanation
QUnit (Jasmine, Mocha, etc) first evaluates the arguments, then passes the computed values to assertion functions. Thus the failed assertion has no idea what the failing expression was. This forces you to write assertion messages, repeating the test condition
QUnit;QUnit;qunit-helpful automatically rewrites your tests before QUnit executes them, adding the condition source to the message string. Thus you can skip writing the same stuff
QUnit;// will be evaluated by QUnit as// QUnit.ok(2 + 2 === 4, 'ok 2 + 2 === 4');QUnit;// will be evaluated by QUnit as// QUnit.equal(foo('a', 1), 'foo-a-1', 'equal "foo('a', 1)" and "foo-a-1"');Unknown or custom assertions will be left unchanged. The source rewriting is done using falafel.
Install
Node:
npm install qunit-helpful --save-dev
// load qunit-helpful before unit tests
$ qunit -c node_modules/qunit-helpful/qunit-helpful.js -t tests.js
Browser:
bower install qunit-helpful
// include the qunit js script first, then
<script src="bower_components/qunit-helpful/qunit-helpful-browser.js"></script>
// then include user tests
Limitations
-
assertargument to the unit test is not supported yet, please useQUnit.equalrather thanfunction (assert) { assert.equal(...); } -
global variables should be ok, but closure variables to the unit test will cause ReferenceError. This is due to the dynamic source code rewriting and evaluation which leads to the test to have a different lexical scope location.
// will cause ReferenceErrorvar foo = 'foo';QUnit;Workaround 1
Skip dynamic test rewriting in this case by adding suffix noHelp or no_help to the test
function name
var foo = 'foo';QUnit;Workaround 2
If you need external non-global variables, use qunit-inject to inject them. Load qunit-inject before qunit-helpful and it should work.
QUnit;QUnit;Related
Other QUnit plugins I wrote:
There is a different approach to improving assertion messages: grab the
detailed callsite as
better-assert does. Unfortunately,
this is limited to V8 javascript engine only. My approach should work with almost
any modern javascript engine (as long as it supports correct function toString method).
Small print
Author: Gleb Bahmutov © 2014 @bahmutov
License: MIT - do anything with the code, but don't blame me if it does not work.
Support: if you find any problems with this module, email / tweet / open issue on Github