front-orm
The package is designed for easy-to-use receipt, storage, refreshing and updating of data received from the server
Installation
npm install front-ormQuick Start
npm install front-ormImporting
import {EntityManager} from "front-orm";Create entity manager
const em = new EntityManager(/* setReactivity */)You can add object tracking or a reactivity creation function. For example, use watch-object
npm install watch-objectimport {watch} from "watch-object";
const setReactivity = (data) => {
if (!Array.isArray(data)) {
watch(data, 'name', (newVal, oldVal) => {
console.log('obj name set', newVal, ' oldVal:', oldVal)
})
}
return data
}Create models
// You can also import fields classes
const PrimaryKey = em.defaultClasses.fields.PrimaryKey
const StringField = em.defaultClasses.fields.StringField
const NumberField = em.defaultClasses.fields.NumberField
const CollectionField = em.defaultClasses.fields.CollectionField
const EntityField = em.defaultClasses.fields.EntityField
function Author(em) {
return {
id: new PrimaryKey(em),
name: new StringField(em),
age: new NumberField(em),
books: new CollectionField(em, 'Book')
};
}
function Book(em) {
return {
id: new PrimaryKey(em),
name: new StringField(em),
author: new EntityField(em, Author.name),
};
}Add a model to the Entity manager
// You can also import classes
const Collection = em.defaultClasses.types.Collection
const Entity = em.defaultClasses.types.Entity
em.setModel(Author, {
find: new Entity(em, (value) => {
// Your request to the server
return responseData
}),
})
em.setModel(Book, {
findSomeThing: new Collection(em, (value) => {
// Your request to the server
return responseData
}),
})Add hooks that will be used for all models
em.setHooks({
get(model, pk) {
/*
Your request to the server
return the data corresponding to the model
*/
},
create(modelData, value) {
/*
Your request to the server
return the primary key
*/
},
update(modelData, value) {
/*
Your request to the server
return the primary key
*/
},
delete(modelData, pk) {
/*
Your request to the server
return the primary key
*/
},
})Use package api
const author = await em.repositories.Author.find(authorParams)
const booksCollection = await em.repositories.Book.findSome(bookParams)
const book = booksCollection[0]
const newAuthor = em.post(someNewValue, em.models.Author)
em.put(someUpdatingValue, book)
em.flush()Demo
or
git clone https://github.com/bd2051/front-orm-quick-example.git
cd front-orm-quick-example
npm install
npm run serveOverview
The main goal of the library is to quickly create a data processing system from a server with Restful API. The library is suitable for small applications and prototypes.
The data storage uses an ORM design. When calling the missing property, data is requested from the server.
The library implies the use of data reactivity but does not contain it.
For full implementation, signals from the server about updating data are required. Use websockets, sse or long/short polling.
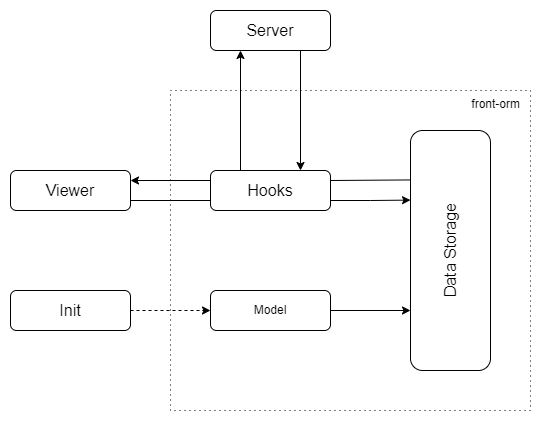
The scheme of the library is shown in the figure
Model
To initialize the model, you need to create a model function that returns a set of model fields
function Book(em) {
return {
id: new PrimaryKey(em),
name: new StringField(em),
page: new NumberField(em),
stories: new CollectionField(em, 'Story', (value) => value.id),
author: new EntityField(em, 'Author', (value) => value.id)
};
}The function name is used as the model name.
Fields classes
For all fields, the first parameter is an instance of the entity manager.
PrimaryKey is a required field. Used for identification and requests.
StringField is used for a regular string field.
NumberField is used for a regular number field. Currently, no different from StringField.
BooleanField is used for a boolean field. Currently, no different from StringField. See Why beta
CollectionField is used to associate OneToMany or ManyToMany with another entity.
The second parameter is the name of the associated entity.
The third parameter is a function for bringing an entity object to the primary key. By default
(pk) => pkExample:
Data received from the server for the entity Book
const book = {
id: 1,
stories: [{id: 1}, {id: 10}, {id: 11}],
...otherFields
}Then the function should look like this
const convertValueToPk = (value) => value.idIf the data from the server looks like this
const book = {
id: 1,
stories: [1, 10, 11],
...otherFields
}you can use the default function
(pk) => pkEntityField is used to associate OneToOne or ManyToOne with another entity. The parameters are similar to CollectionField.
Model initializing
To initialize the model, there is a setModel method
em.setModel(Book, {
find: new Entity(em, (value) => {
// Your request to the server
return responseData
}),
findAll: new Collection(em, (value) => {
// Your request to the server
return responseData
}),
})The first parameter is a model function
The second parameter used to create a model repository. It is an object with the Entity and Collection classes
Entity and Collection are classes for determining the response from the server.
For both classes, the first parameter is an instance of the entity manager, and the second is a callback with custom requests to the server. The callback parameter can be any.
Callback response:
- for Entity, an object with model fields must be returned
- for Collection, an array of objects with model fields must be returned
Repository
The Repository stores all methods of getting data from the server added during initialization of the model.
Getting access to the Repository
const repository = em.repositories[modelName]or
const repository = em.getRepository(modelName)Public properties and methods:
- $em - instance of the entity manager
- $model - instance of Model
- $refreshCollection - a method for getting refreshed data from the server
Data storage
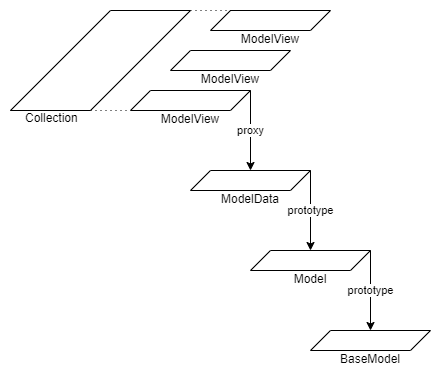
The main interaction with data occurs through the ModelView and the ModelView collection.
The structure of the data storage object is shown in the figure.
The BaseModel contains methods used at higher levels.
- $em is an instance of the entity manager
- $getName is a function that returns the model name
- $getPkName is a function that returns the name of the primary key
- $refresh is a function for refreshing data from the server
- $get, $create, $update, $delete calls the corresponding entity manager hook
The Model object is created when initializing the model function based on the prototype BaseModel. Contains the same fields as the model function.
The ModelData object is the main data storage element. Based on the prototype Model. Filled with data from the server based on the model fields. A link to the corresponding ModelData is placed in the relationship field. If there is no data, an instance of the class Empty is assigned to the field.
ModelView is based on the Proxy class with the ModelData target object. When accessing properties, either the value of the target object field or the ModelView of the associated object is returned. If the value of the target object field is equal to an instance of the Empty class, the 'get' hook is called. The assignment operation does not work, use the put method of the entity manager to change the data.
ModelView collection is an array of ModelView objects. Using the methods 'push', 'pop', 'shift', 'unshift' will cause an error. To change the data, the put method of the entity manager is used
Garbage collection
Memory is freed automatically by the garbage collector and does not require additional actions from the programmer. To do this, most of the internal relationships between data are implemented on the basis of WeakSet, WeakMap and WeakRef. Thus, the only live references to the data are ModelView and ModelView collection obtained using the entity manager. Excluding them from memory is a condition for starting the garbage collector for this data.
Note: The js garbage collector has a complex logic of operation, so even without live references, the object can continue to be in memory for some unspecified time.
Hooks
list of hooks used:
- preFlush
- get
- create
- update
- delete
All hooks except 'get' are triggered during the execution of the 'flush' method. 'Get' is run in all cases when the Data Storage did not have the necessary data.
preFlush is designed for manipulating commits before launching the rest of the hooks. Read more about commits below.
- The input parameter is an array of commits.
- Waiting for the return of an array of commits or an empty array
get is used to get missing data in ModelData
- Input parameters:
- Model
- primary key
- Waits for the return of an object with fields similar to the Model
create is designed to send information about the creation of new data.
- Input parameters:
- ModelData
- generalized value obtained from the commits for a given modelData
- Waiting for the primary key to be returned
update is designed to send information about the updating of data. Similar to create
delete is designed to send information about data deletion
- Input parameters:
- ModelData
- primary key
- Waiting for the primary key to be returned
Commits
All up-to-date information about changes in model data is stored in commits. This allows you to roll back changes within certain limits. Updating of the model data with server data occurs by the 'flush' method. At the same time, all commits are overwritten. During execution, heuristic logic determines the use of appropriate hooks for commits. Depending on the specifics of data processing by the server, you may need to change the logic. There is a preFlash hook for this. It can also be used to create batch requests. Returning an empty array will result in the remaining hooks not being started.
Entity Manager
The main element of the api library is the entity manager
Creating:
const em = new EntityManager(setReactivity);The input parameter is optional and is intended to create ModelData reactivity. Read more about reactivity below.
Public properties of the EntityManager:
- models
- repositories
- pending
- removed
- defaultClasses
models contains instances of all available Models. Needed for some methods
repositories contains all the methods added during initialization of the Model. It has a tree-like structure. At the first level, the names of the models. On the second methods
The pending value is substituted for the waiting time for a response from the server. By default, null.
The removed value is substituted if the ModelData has been removed. By default, undefined.
defaultClasses contains all public classes available in the library. These classes can be imported from the library.
Public methods of the EntityManager:
- setHooks
- setModel
- getModel
- getRepository
- onAddModelData
- onAddCollection
- put
- post
- remove
- flush
- revert
- revertAll
- checkModelDataByPk
setHooks is designed to add all entity manager hooks. Read more here
setModel is designed to add models to the entity manager. Read more here
getModel and getRepository return the Model and repository of the Model, respectively. Input parameter model name.
onAddModelData and onAddCollection are handlers designed to organize messaging with the server. Read more here
put is the main method for changing model data
- Input parameters:
- an object with properties that need to be changed
- ModelView or Model (To create the input parameter Model)
- ModelView is returned
Example:
const book = em.repositories.Book.find(1)
console.log(book.name) // 'Old book name'
em.put({
name: 'New book name'
}, book)
console.log(book.name) // 'New book name'post wrapper over the put method. Intended only for creating.
- Input parameters:
- an object with properties similar to the Model
- Model
- ModelView is returned
Example:
const newBook = em.post({
name: 'Created book',
...otherProperties
}, em.models.Book)
console.log(newBook.name) // 'Created book'remove wrapper over the put method. Intended only for deleting.
- The only input parameter is ModelView
- ModelView is returned
flush starts the processes for sending data to the server. Read more here
revert rolls back model data changes. The only input parameter is the number of commits being rolled back. By default, one. Read more here
revertAll this wrapper over the revert method. Designed to roll back all changes.
checkModelDataByPk is a method that checks ORM data exists by pk.
- Input parameters:
- Model
- Primary key
- Boolean is returned
Reactivity
The library implies the use of reactivity, but it does not have it itself. To add reactivity as an input parameter when creating an entity manager, add the function. The function will be called every time ModelData or ModelView collection is created
const setReactivity = (data) => {
// do something to make the data reactive
return reactiveData
}
const em = new EntityManager(setReactivity);At the moment, reactivity works exactly when using Vue 3. See Why beta
Example with Vue 3
import { EntityManager } from 'front-orm';
import { ref } from 'vue';
const em = new EntityManager((modelData) => ref(modelData).value);Real-time update
For a full real-time update, you need to establish negative feedback with the server. This is especially true for collections. You can use websockets, server events, or long/short polling for this.
Example based on websockets
const ws = new WebSocket(URL)
const em = new EntityManager()
em.onAddModelData = (model, pk) => {
ws.send(JSON.stringify({
model: model.$getName(),
id: pk
}))
}
const collectionsMap = new Map()
em.onAddCollection = (repository, weakCollection) => {
ws.send(JSON.stringify({
model: repository.$model.$getName(),
isCollection: true
}))
if (typeof collectionsMap.get(name) === 'undefined') {
collectionsMap.set(name, []);
}
collectionsMap.get(name).push({weakCollection, repository});
}
ws.addEventListener('message', (message) => {
const { model: modelName, id } = JSON.parse(wsMessage.data);
const updatingCollections = collectionsMap.get(modelName) || [];
updatingCollections.forEach(({weakCollection, repository}) => {
const collection = weakCollection.deref();
if (typeof collection === 'undefined') {
return;
}
repository?.$refreshCollection(collection);
});
em.getModel(modelName).$refresh(id)
})onAddModelData is called when ModelData is created
- Input parameters:
- Model
- primary key
ModelData is not passed so as not to break the logic of garbage collection. Read more here
onAddCollection is called when collection is created
- Input parameters:
- Repository. Read more here
- WeakCollection. It is WeakRef with collection target
Use the 'deref' method to interact with the collection.
When receiving a message from the server about data changes, use the $refresh method of the Model and $refreshCollection of the Repository
Why beta version
Even though the idea of the library is simple, the implementation revealed certain difficulties. For the stable version, there is not enough experience in the practical use of the library.
Using the library with frameworks other than vue 3 may result in structure changes. Some solutions applied are not final. For example, the StringField, Number Field, and BooleanField classes all look the same. Perhaps they will be replaced by a single field.
I intend to support the project and hope for feedback from using the library.